Elevating Materials to a New Level
For years, alternatives to materials that harm our ecosystem have been sought. Leather has a significant environmental impact, but the options to replace leather fall short of industry needs. Until now.
Elevating Materials to a New Level
For years, alternatives to materials that harm our ecosystem have been sought. Leather has a significant environmental impact, but the options to replace leather fall short of industry needs. Until now.
Embrace Innovation
for True Sustainability
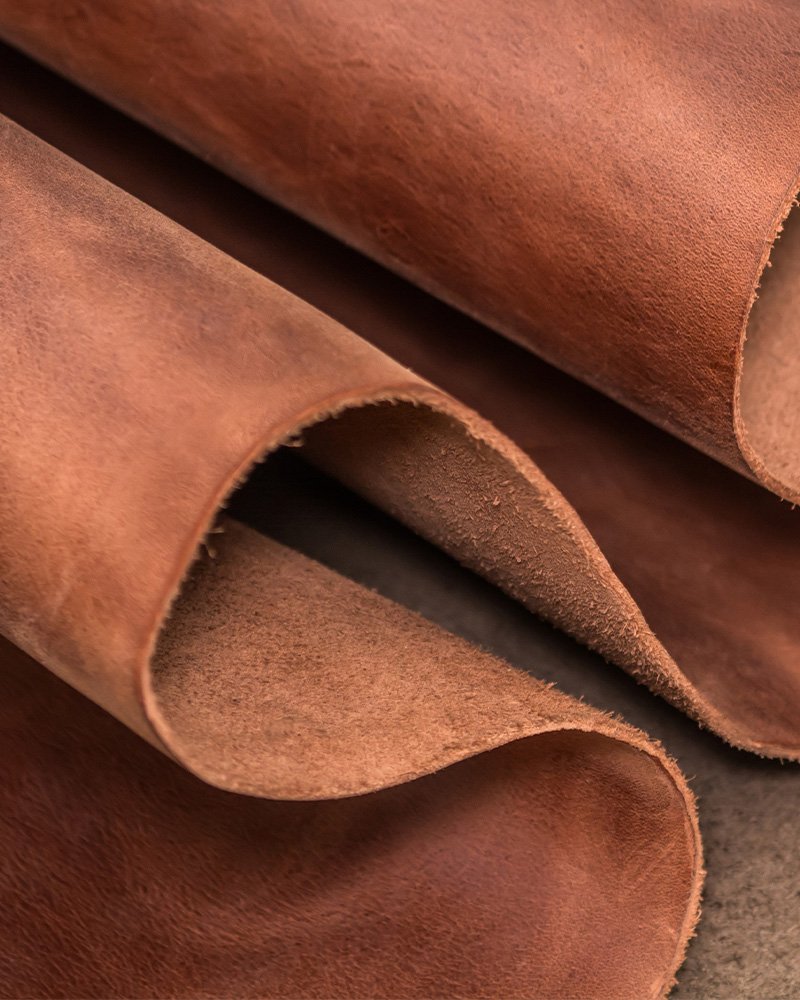
Contrary to the way standard leather is manufactured, ELEVATE is produced using a green process.
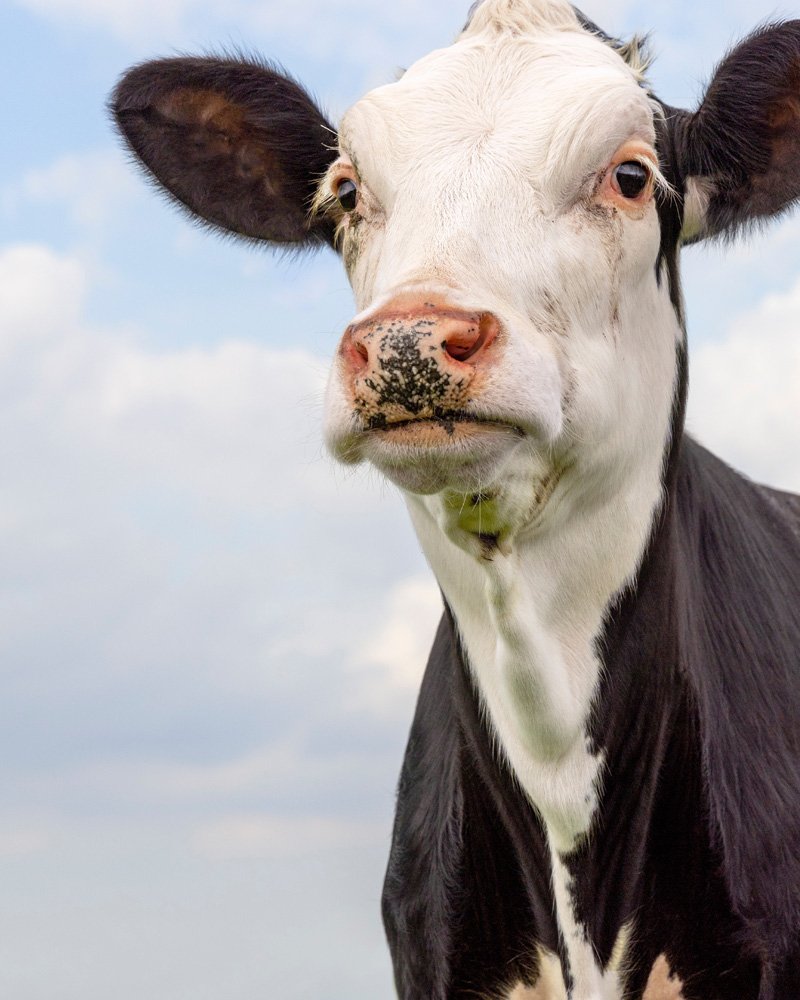
Animal Leather
ELEVATE



Animal Leather
ELEVATE
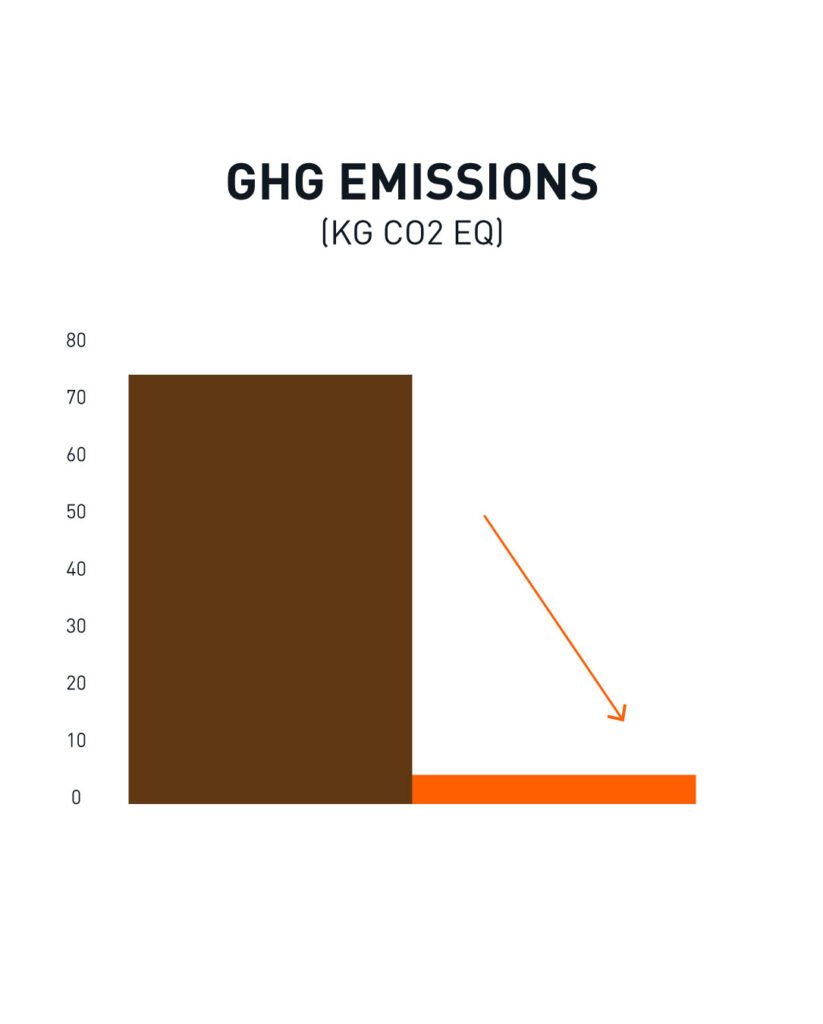
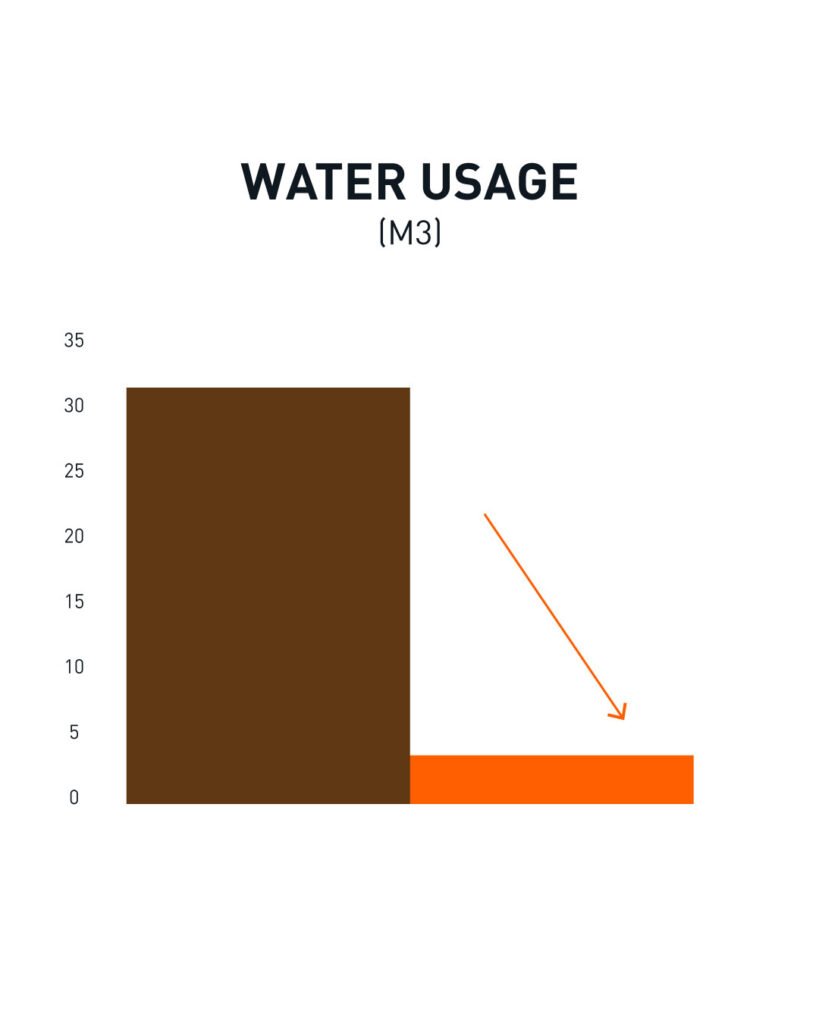
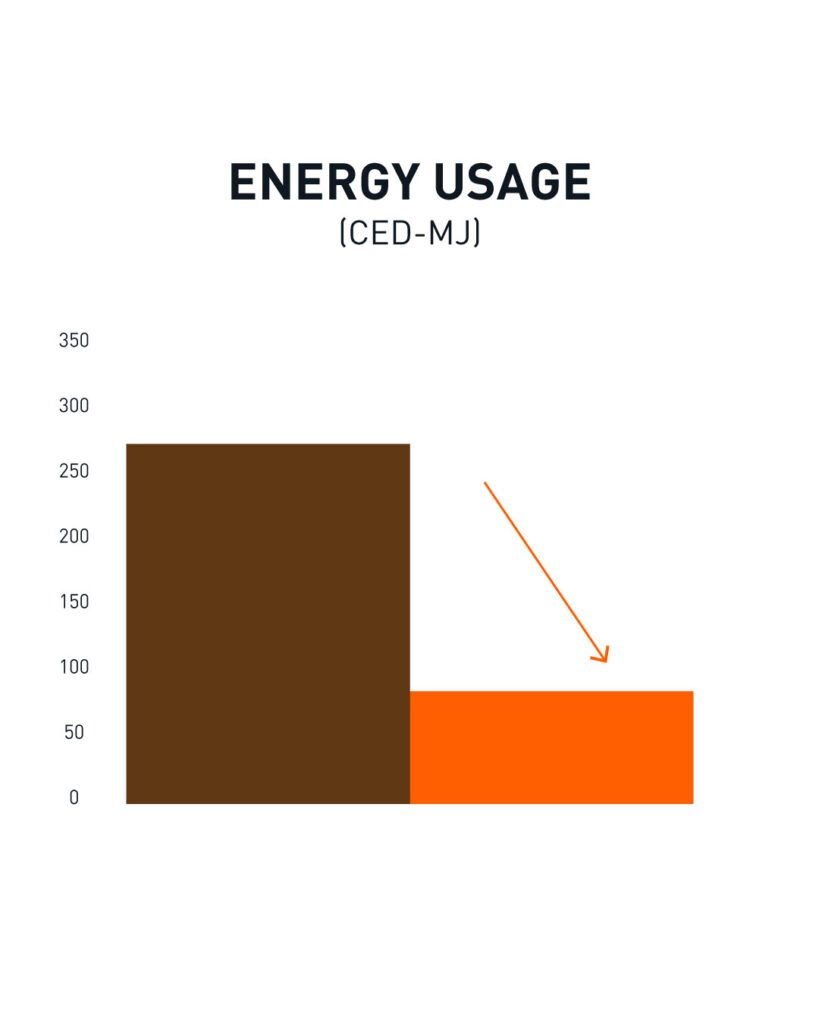
The Life Cycle Analysis of ELEVATE was conducted by an independent third party.
The aim of the study was to generate reliable and accurate quantitative environmental data impact results for the production of one square meter of ELEVATE. This study measures the direct environmental impact over the system boundary of cradle-to-gate, including raw materials, transport of raw materials and manufacturing.
In comparison to animal leather, ELEVATE emits significantly less greenhouse gasses and uses substantially less water and energy.
Earth-Friendly
End of Life
We had an independent 3rd party perform comprehensive biodegradability tests under various soil and composting conditions.
We tested two variations of our customizable formulation for ELEVATE.
One formulation had degraded 33% and the other had degraded 70% in just six months, proving that we can not only tune the look and feel, but also customize the performance and degradability to meet your needs.
Impact Matters
Environmental
and Ethical
Leather is a material used for thousands of years, but the industrialization of leather turned a once natural material into a process requiring harmful chemicals and plastic finishing.
Costs of Leather
Impact Matters
Environmental and Ethical Costs of Leather
Leather is a material used for thousands of years, but the industrialization of leather turned a once natural material into a process requiring harmful chemicals and plastic finishing.
Separating Myth from Fact:
What You Need to Know
MYTH
FACT
MYTH
FACT
MYTH
FACT
MYTH
FACT




FACTS
FACTS
FACTS
FACTS
Many people believe leather is simply a byproduct of the meat industry. Leather is a significant co-product, not a byproduct. It accounts for a substantial portion of the profits from the slaughter of animals. High-quality skins are often the primary reason animals are bred, especially in the case of exotic leathers.
Leather is often marketed as natural and more environmentally friendly than synthetic alternatives.The process of tanning leather is highly pollutive. It involves toxic chemicals like chromium, which can harm aquatic life and pollute water bodies. The overall environmental impact includes high carbon emissions and significant water usage.
The tanning process heavily treats animal hides with chemicals, preventing them from decomposing naturally. Buried leather can take 50 years or more to decompose and treated leather might not decompose at all.
On it’s own, animal leather scratches easily and is not water resistant. Therefore, almost all leather is coated in plastic.
Hidden
Realities
of Animal
Leather
Resource
Intensive
Producing animal leather requires large amounts of feed, land, water, and energy. It is associated with deforestation, biodiversity loss, and high methane emissions from cattle.
High Water
Usage
The production of one kilogram of leather requires up to 17,000 liters of water, mainly due to the water-intensive nature of animal rearing and the tanning process.
Contribution
to Pollution
Traditional leather tanning uses harmful chemicals, including chromium and other heavy metals which are dangerous to both human health and the environment. Tannery effluents lead to soil and water pollution extensively.
Impact on
Human Health
Workers in the leather industry often face poor working conditions and are exposed to toxic chemicals that can lead to serious health issues, including cancer, skin diseases, and respiratory problems.
Ethical
Concerns
The leather industry is also fraught with ethical issues, involving the slaughter of animals, often under inhumane conditions, and the use of skins from endangered species which contributes to biodiversity loss.
